The Data Center Professionals Network
The Global Database of Data Center Industry Expertise
Introduction to Software Development Life Cycle: Phases & Models
SDLC stands for Software Development Life Cycle. It is a process that gives a complete idea about developing, designing, and maintaining a software project by ensuring that all the functionalities along with user requirements, objectives, and end goals are addressed. With SDLC, the software project’s quality and the overall software development process get enhanced.
 Benefits of SDLC
Benefits of SDLCFor any software project, SDLC offers the following benefits
- With SDLC, one can address the goals and problems so that the project is implemented with the highest precision and accuracy
- In SDLC, the project members cannot proceed ahead before completion & approval of the prior stages
- Any installation in the project that has been executed using the SDLC has necessary checks so that it is tested with precision before entering the installation stage
- With a well-defined SDLC in place, project members can continue the software development process without incurring any complications
- SDLC offers optimal control with minimum problems, allowing the project members to run the project smoothly
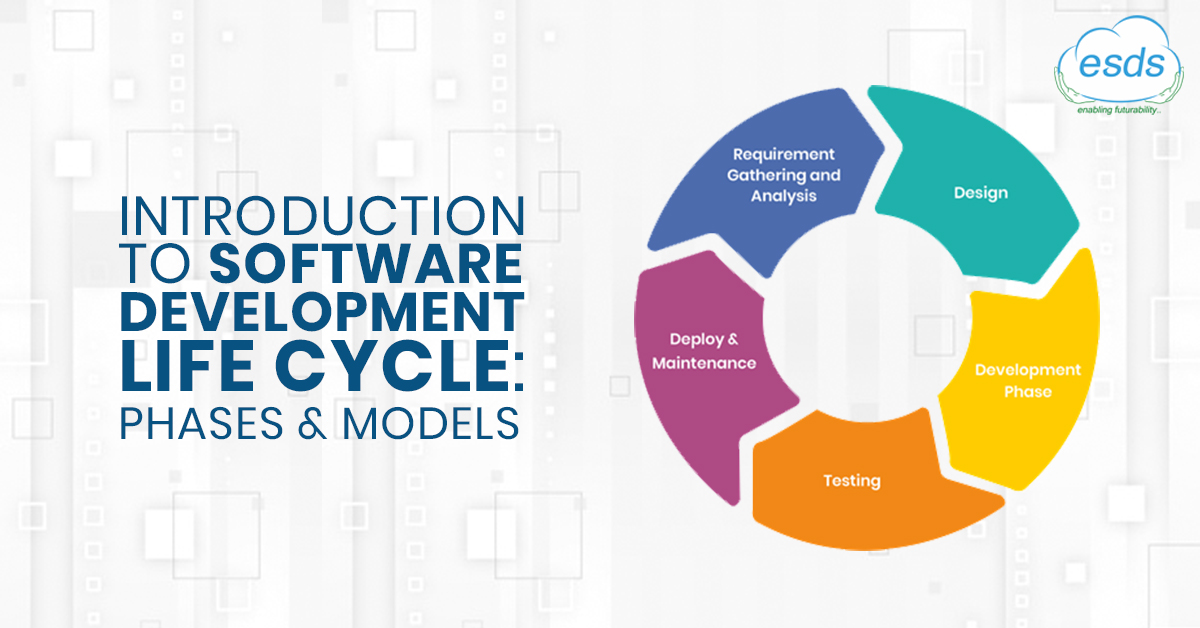
Stages of SDLC
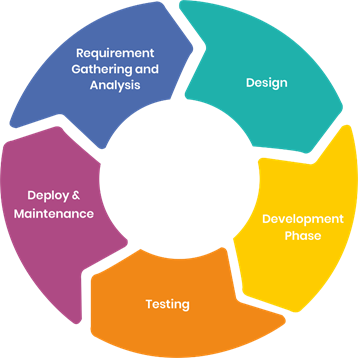 SDLC Stages
SDLC StagesStage 1: Requirement Gathering & Analysis Phase
In an SDLC, this is the first and most crucial phase for a software project’s success. In this phase, communication takes place between stakeholders, end-users, and project teams, as both functional and non-functional requirements are gathered from customers.
The Requirement Gathering & Analysis Phase of SDLC involves the following
- Analysis of functionality and financial feasibility
- Identifying and capturing requirements of stakeholders through customer interactions like interviews, surveys, etc.
- Clearly defining and documenting customer requirements in an SRS (Software Resource Specification Document) comprising of all product requirements that need to be developed
- Creating project prototypes to show the end-user how the project will look
Stage 2: Design Phase
In the design phase of an SDLC, the architectural design is proposed for the project based on the SRS Document requirements.
The Designing Phase of SDLC involves the following
- Separation of hardware and software system requirements
- Designing the system architecture based on gathered requirements
- Creating Unified Modelling Language (UML) diagrams like- use cases, class diagrams, sequence diagrams, and activity diagrams
Stage 3: Development Phase
In the entire SDLC, the development phase is considered to be the longest one. In this phase, the actual project is developed and built.
The Development Phase of SDLC involves the following
- Actual code is written
- Demonstration of accomplished work presented before a Business Analyst for further modification of work
- Unit testing is performed, i.e., verifying the code based on requirements
Stage 4: Testing Phase
Almost all stages of SDLC involves the testing strategy. However, SDLC’s testing phase refers to checking, reporting, and fixing the system for any bug/defect. In this phase, the on-going system or project is migrated to a test environment where different testing forms are performed. This testing continues until the project has achieved the quality standards, as mentioned in the SRS document during the requirement gathering phase.
The Testing Phase involves the following-
- Testing the system as a whole
- Performing different types of test in the system
- Reporting and fixing all forms of bugs & defects
Stage 5: Deployment & Maintenance Phase
In this SDLC phase, once the system testing has been done, it is ready to be launched. The system may be initially released for limited users by testing it in a real business environment for UAT or User Acceptance Testing.
The Deployment & Maintenance Phase involves the following-
- The system is ready for delivery
- The system is installed and used
- Errors are rectified that might have been previously missed
- Enhancing the system inside a data center
SDLC Models
Various SDLC models are defined and designed to follow the software development process. These models are also known as Software Development Process Models. Each of these models follows a series of steps for ensuring the complete success of a project.
Some of the most popular SDLC models used for software development include-
- Waterfall Model
- Iterative-Incremental Model
- Spiral Model
- Agile Model
- Rapid Action Development (RAD) Model
Waterfall Model
This model is the most commonly used SDLC model. In this model, each phase starts only after the previous step has been completed. This is a linear model having no feedback loops.
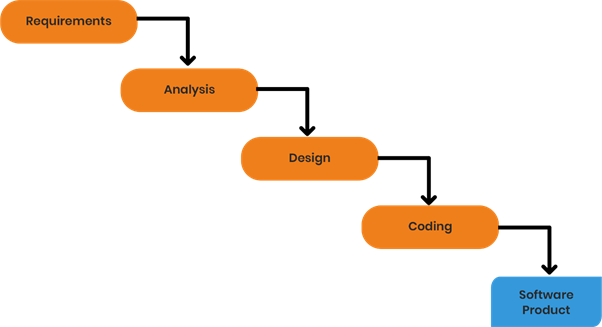 Waterfall Model
Waterfall ModelStrengths of the Waterfall Model
- Easy to understand and use
- Achievements are well-defined
- Defines requirements stability
- Works well when the project quality is important
Weaknesses of the Waterfall Model
- It cannot match reality well
- Difficult to make changes
- Software delivered towards the end of the project only
- Testing begins only after the development phase is complete
Iterative-Incremental Model
In this model, in the initial stages, a partial implementation of the complete system is constructed such that it will be present in a deliverable form. Increased functionalities are added and for any defects, they are fixed with the working product delivered at the end. This process is repeated until the product development cycle gets completed. These repetitions of processes are known as iterations. With each iteration, a product increment gets delivered.
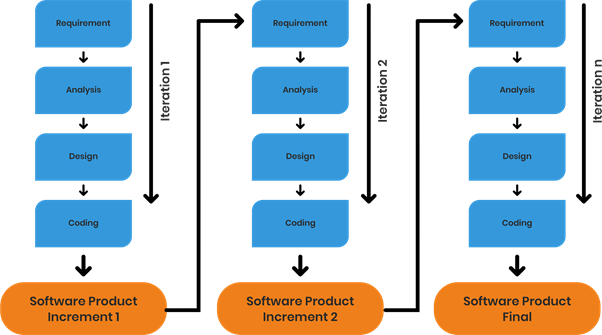 Iterative-Incremental Model
Iterative-Incremental ModelStrengths of Iterative-Incremental Model
- Prioritized requirements can be initially developed
- The initial delivery of the product is faster
- Lower initial delivery costs
- Changes in requirements can be easily adjusted
Weaknesses of Iterative-Incremental Model
- There are requirements for effective iterations planning
- Efficient design is required for including the required functionalities
- An early definition of a complete, as well as fully functional system, is needed for allowing increments definition
- Clear module interfaces are required
Spiral Model
The spiral model combines risk analysis along with RAD prototyping to the Waterfall model. Each of the cycles has the same steps as in the case of the Waterfall model.
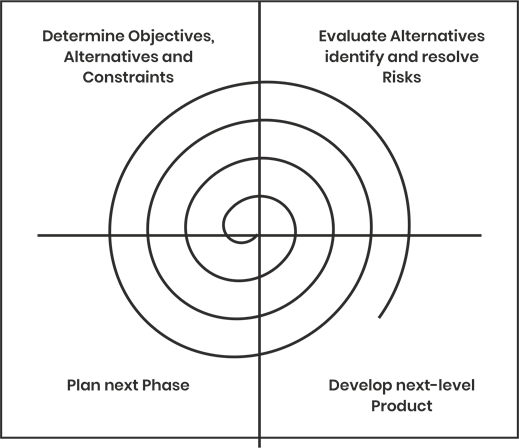 Spiral Model
Spiral ModelThe spiral model has 4 quadrants, namely- Determine Objectives, Alternatives and Constraints (Quadrant 1), Evaluate Alternatives, Identify and Resolve Risks (Quadrant 2), Develop Next-Level Product (Quadrant 3) and Planning the Next Phase (Quadrant 4).
Strengths of the Spiral Model
- An early indication of the risks can be provided, without incurring much cost
- Users can have a look at their system early due to rapid prototyping tools
- Users are involved in all lifecycle stages
- Critical & high-risk functionalities are initially developed
Weaknesses of the Spiral Model
- It may be hard to set the objectives, verifiable milestones for indicating preparedness to go ahead with the next iteration
- Time spent on addressing risks can be large for smaller & low-risk involved projects
- The spiral model can be complex to understand for new members
- The spiral may go on indefinitely
Agile Model
The agile model is the combination of the iterative-incremental model that depends on process adaptability along with customer satisfaction through the delivery of software products. In this model, the project is broken down into smaller time frames for delivering certain features during a release.
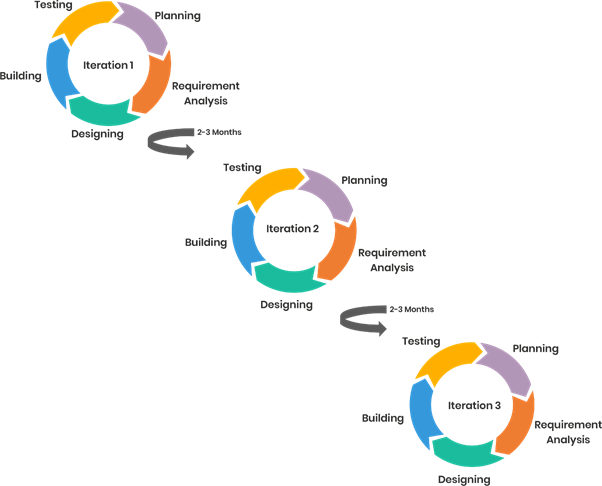 Agile Model
Agile ModelStrengths of the Agile Model
- Easy to accommodate changing requirements
- Regular communication takes place between customers and developers
- Functionalities can be developed quickly and demonstrated to customers
Weaknesses of the Agile Model
- Not ideal for handling complex dependencies
- Teams need to have the desired experience levels for adhering method rules
Rapid Application Development (RAD) Model
The RAD SDLC model is based on prototyping and iterative development, with no involvement of a defined planning structure. In this model, different function modules are parallelly developed as prototypes and then integrated to speed up product delivery.
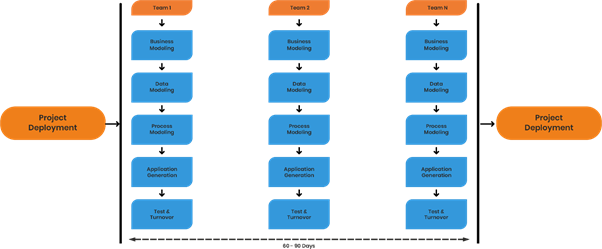 RAD Model
RAD ModelStrengths of RAD Model
- Reduced cycle time and enhanced productivity with minimal team members
- Customer’s continuous involvement ensures minimal risks of not achieving customer satisfaction
- Easy to accommodate any user changes
Weaknesses of RAD Model
- Hard to use and implement with legacy systems
- Heavily dependent on technically strong members for identifying business requirements
Welcome to
The Data Center Professionals Network
Connecting data center industry professionals worldwide. Free membership for eligible professionals.
Events
Follow Us
© 2026 Created by DCPNet Admin.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of The Data Center Professionals Network to add comments!
Join The Data Center Professionals Network